PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC ARRAY - PLA
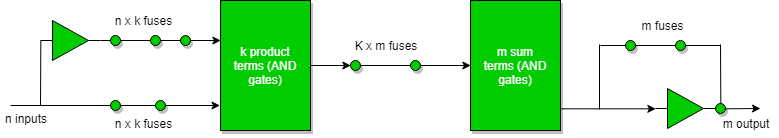
Programmable Logic Array(PLA) is a fixed architecture logic device with programmable AND gates followed by programmable OR gates. PLA is basically a type of programmable logic device used to build a reconfigurable digital circuit. PLDs have an undefined function at the time of manufacturing, but they are programmed before being made into use. PLA is a combination of memory and logic.
PLA is similar to a ROM in concept; however, it does not provide full decoding of variables and does not generate all minterms as in the ROM.
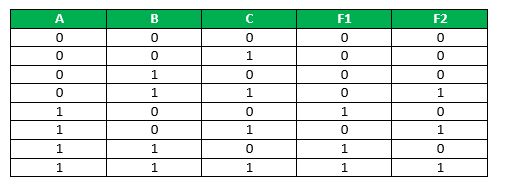
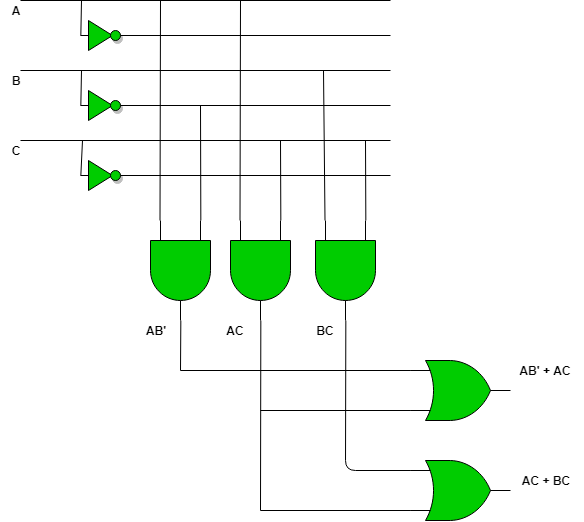
In PLA, all the minterms are not realized but only required minterms are implemented. As PLA has a programmable AND gate array and a programmable OR gate array, it provides more flexibility but the disadvantage is, it is not easy to use
PROGRAMMABLE ARRAY LOGIC - PAL
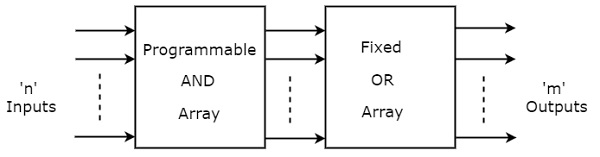
Programmable Array Logic (PAL) is a commonly used programmable logic device (PLD). It has programmable AND array and fixed OR array. Because only the AND array is programmable, it is easier to use but not flexible as compared to Programmable Logic Array (PLA). PAL’s only limitation is number of AND gates. PAL consist of small programmable read only memory (PROM) and additional output logic used to implement a particular desired logic function with limited components.
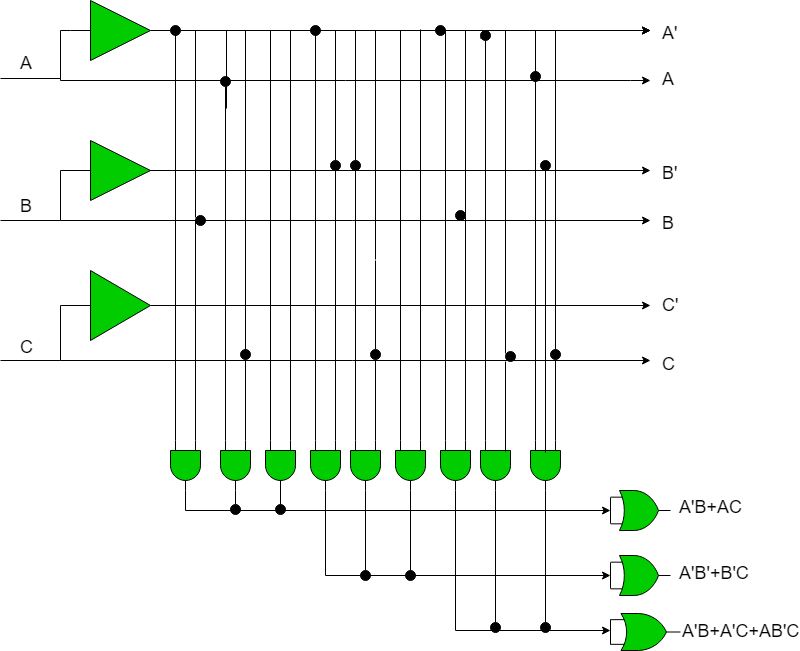
COMPLEX PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC DEVICE - CPLD
A complex programmable logic device (CPLD) is a programmable logic device with complexity between that of PALs and FPGAs, and architectural features of both. The main building block of the CPLD is a macrocell, which contains logic implementing disjunctive normal form expressions and more specialized logic operations.
Macrocells are functional blocks that perform combinatorial or sequential logic, and also have the added flexibility for true or complement, along with varied feedback paths.
FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAY - FPGA
A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is a type of integrated circuit that can be programmed or reprogrammed after manufacturing. It consists of an array of programmable logic block and interconnects that can be configured to perform various digital functions. FPGAs are commonly used in applications where flexibility, speed, and parallel processing capabilities are required, such as in telecommunications, automotive, aerospace, and industrial sectors.
FPGA configuration is generally specified using a hardware description language (HDL), similar to that used for an application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC). Circuit diagrams were previously used to specify the configuration, but this is increasingly rare due to the advent of electronic design automation tools.